
Interphase: The cell is not dividing at this time period. It simply represents an area where the sister DNA molecules (chromatids) are attached.ġ.
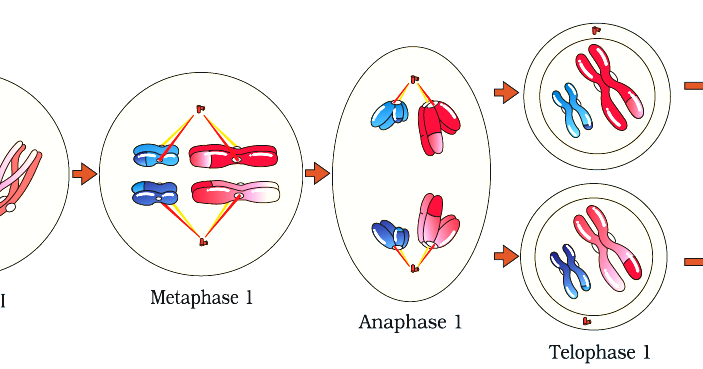
In these greatly oversimplified illustrations, the centromere is shown as a black dot. The chromatids (DNA molecules) are attached in a region known as the centromere. Each chromatid is essentially composed of a greatly coiled DNA molecule and protein. Each protein bead with DNA on its surface is called a nucleosome. Each protein bead contains about 200 base pairs on its surface, while the strand between consists of about 50 base pairs. One chromatid of this eukaryotic chromosome doublet is unravelled, showing a twisted DNA molecule wrapped around beads of histone protein. Since there are 2 sets of chromosomes in this diagram, the cell is diploid (2n). Three blue chromosomes (a, b & c) in this cell represent one haploid set of paternal chromosomes from the father. Three pink chromosomes in this cell (A, B & C) represent one haploid set of maternal chromosomes from the mother. One member of each pair comes from the mother (pink chromosome) and one member of each pair comes from the father (blue chromosome). Each pair is called a homologous pair because they are matching in size and shape. Chromosomes A & a represent one pair, B & b represent a second pair, and C & c represent a third pair. Since the cell contains a total of 6 chromosomes, it has a chromosome number of 6. In this diagram the cell contains 3 pairs of homologous single chromosomes, a total of 6 chromosomes. The single chromosomes become doubled again during the S-phase of interphase, prior to the onset of prophase. After the chromatids separate during anaphase and the cell divides during telophase, the resulting daughter cells have 23 pairs of single chromosomes, a total of 46. In a human cell during prophase there are 23 pairs of homologous chromosome doublets, a total of 46 doublets and 92 chromatids. In this diagram there are two pairs of homologous chromosome doublets. Homologous pairs of doublets are represented by one large pink and one large blue doubled chromosome of matching size, and one small pink and one small blue doublet of matching size. Fertilization of the two haploid sex cells (egg and sperm) results in a diploid zygote (n + n = 2n).

Diploid (2n) organisms such as humans have two sets of chromosomes, one haploid (n) set from the father and one haploid (n) set from the mother. The striped blue doublets represent a set of paternal doubled chromosomes originally from the father's sperm. The clear pink doublets represent a set of maternal doubled chromosomes originally from the mother's egg. Beginning with prophase, the chromosomes appear as doublets. Single chromosomes and doubled chromosomes (chromosome doublets).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
